Mapping Land Subsidence using GIS and Remote Sensing
About Course
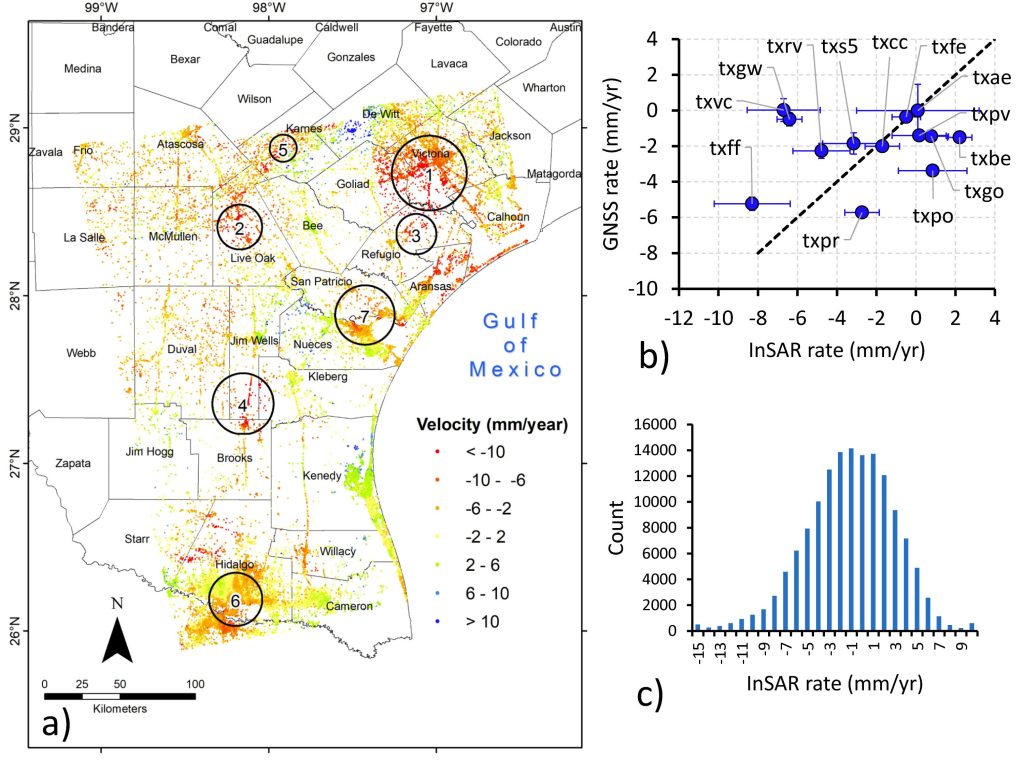
Interferometry is a geodetic technique that calculates the interference pattern caused by the difference in phase between two images acquired by a space-borne Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system at two distinct times. InSAR makes use of the difference in phase between two radar scenes to determine precise differences in range to a target and to subsequently determine the exact surface location, and subtle changes in topography. The module covers the use of radar data to map areas affected by land subsidence and quantify the subsidence rates. This module will specifically cover radar remote sensing, principles of radar interferometry, limits of interferometric measurements, and constructing and improving interferograms.
Period:
- Two weeks (condensed module)
- Four weeks (full module)
Contents:
- Electromagnetic waves
- Radar sensors
o Passive
o Active
- Polarization
- Synthetic Aperture Systems (SAR)
- Doppler Effect
- Resolution
o Range
o Azimuth
- Radar Equation
- Radar backscatter
- Radar Interferometry
- Interferograms generation
o Baseline estimation,
o Interferogram generation,
o Coherence and adaptive filtering,
o Phase unwrapping,
o Orbital refinement,
o Phase to height conversion and geocoding, and
o Phase to displacement conversion.
Participants will develop software-oriented skills on how to:
- Read, process, and explore radar images.
- Use radar interferometry and define limits of interferometric measurements.
- Construct and improving interferograms using different radar images (i.e., ENVISAT, ERS) applying two pass, three pass, SBAS, permanent scaterer techniques.
- Apply interferometry to quantify land deformation.
Student Ratings & Reviews
No Review Yet
Details
- category
- October 22, 2024 Last Updated
